Clinical Information:
Of the three major estrogens (estrone [e1], estradiol [e2], estriol [e3]), is the least potent natural estrogen (E2 > E1 > E3). In men and non-pregnant women, E1 and E2 are formed from androstenedione and testosterone. E3 is synthesized from E2 and to a limited extent, from 16-alpha metabolites of estrone.
During pregnancy, E3 is the dominant estrogen. The fetal adrenal gland secretes DHEA-S which is converted to E3 in the placenta and enters circulation. E3 levels rise throughout pregnancy, and peak at term.
Measurement of E3 is the diagnosis of maternal-fetal diseases. Decreased second trimester E3 levels have been shown as a marker for Down and trisomy-18 syndromes, as well as gross neural tube defects (anencephaly). Based on these observations, E3 is now part of multplie marker prenatal biochemical screening, along with alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), and inhibin-A measurements (QUAD/Quad Screen (second trimester) Maternal Serum). Low levels of E3 have also been associated with pregnancy loss, Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome (a defect in the biosynthesis of cholesterol), X-linked ichthyosis, and contiguous gene syndrome, aromatase deficiency and primary or secondary fetal adrenal insufficiency.
References:
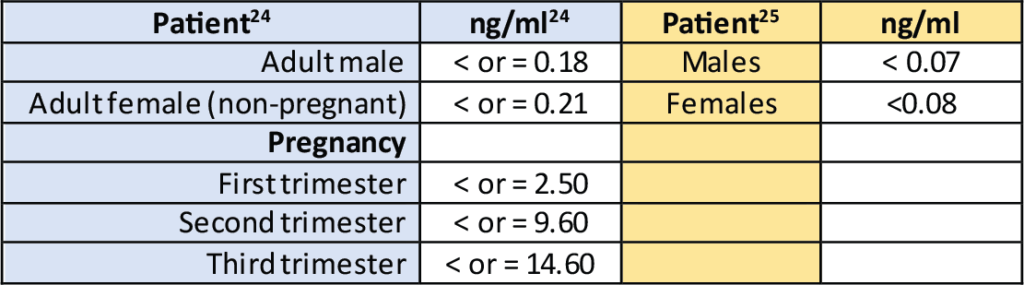
24. http://www.questdiagnostics.com/testcenter/TestDetail.action?ntc=34883
25. http://www.mayomedicallaboratories.com/test-catalog/Clinical+and+Interpretive/81711OCTOBER 4, 2017